Bruises develop after bumps or falls and are a result of ruptured blood vessels under the skin. When these tiny blood vessels tear, a little blood seeps out and gets accumulated in the tissues; it takes form of a bruise and is visible as a purplish or bluish red area on the skin. A small bruise takes two to four weeks to heal completely and bruises on lower parts of the body take longer to disappear.
Common Types of Bruises
Bruises can vary greatly in their size and shape, depending upon the nature and severity of the impact causing them. Most of the bruises heal spontaneously. In order to understand when to worry about a bruise you need to know the different types.
1. Contusions
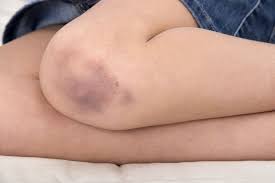
These are the most common bruises that generally form after some blunt trauma. These result from a small collection of blood under the skin and change color with the passage of time. Initially they can be dark red or purple and gradually become green and then yellow before completely disappearing.
2. Hematomas
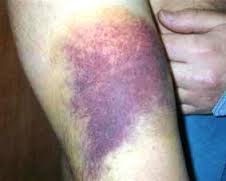
A hematoma is bigger than a contusion and results from a larger amount of blood collection. This can be a result of more severe trauma or surgery. There is swelling and pain associated with hematomas.
Sometimes a blood vessel ruptures spontaneously resulting in a hematoma. If a hematoma develops inside an organ it can be fatal and immediate evaluation is necessary to prevent any complications.
3. Purpura
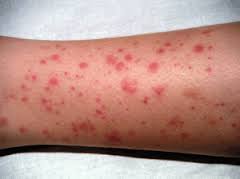
These small purple colored patches develop spontaneously. There is no injury or trauma associated and they can be anywhere on the skin including the oral cavity. The main causes of purpura are reduced coagulation ability or increased vascular fragility. Some medication can also lead to the development of purpura.
When to Worry About a Bruise
Most of us get bruised from time to time. These can be small ones after a bumping into a chair or bigger ones resulting from accidents or sports injuries. While most of the bruises heal spontaneously, there are few situations where a bruise is an indication of some serious underlying problem which must be investigated and treated urgently.
If you notice any of the following, that is when to worry about a bruise and to immediately contact a health care provider:
- If you notice very small multiple bruises (also known as petechiae) without any injury you must contact your doctor urgently. These multiple, 1-3 mm in size, round red spots can be a sign of severe infection, a very low platelet count or heart failure.
- If you hit your head and there is bruising behind your ears, it can be sign of skull fracture.
- A bruise around your belly button can indicate bleeding inside the abdomen.
- Some autoimmune diseases can cause spontaneous bruising. These bruises result from autoimmune injury to blood vessels (where the defense system of the body becomes active against the blood vessels and attacks them).
- You also need to seek immediate medical advice if there is a large bruise on your body and it suddenly becomes very painful. This indicates compartment syndrome, which means that the bruise is putting pressure on the tissues and their oxygen supply is compromised. It has to be treated urgently to avoid life threatening complications.
- Excessive or spontaneous bruising can be a sign of an underlying disease or a bleeding disorder. If you or a loved one gets bruised easily or there are unexplained bruises without any injury it may be due to a bleeding disorder. Common disorders leading to this are clotting factor deficiencies and platelet dysfunction. These conditions are also associated with a history of frequent nose bleeds, excessive bleeding after minor injury, surgery or tooth extraction and very heavy periods.
- Certain diseases like liver disease, cancer, severe infection and cancer can also lead to increased bruising. There can be history of fever, unexplained weight loss, distended abdomen, swollen glands, rash or bone pain.
Treating The Bruises
Bruises generally heal by themselves, if they do not disappear in a couple of weeks then that is when to worry about a bruise. Here are a few tips to ease the pain and speed up the healing process:
- Rest: If you get a bruise give that area some rest. This will stop the bruise from progression.
- Ice: Putting an ice pack on the bruised area greatly reduce the swelling and pain. You can put an ice pack on the bruised area for ten to fifteen minutes three times a day. It is better to avoid putting a hot compress, hot showers, and alcohol for the first couple of days as they may increase swelling. After 2-3 days, you can put ice packs and warm compresses alternatively.
- Compression bandage: Wrapping the bruised limb in a compression bandage can help to decrease the swelling and pain but it must be done very carefully. If it is wrapped too tightly it can do more harm than good.
- Elevated the injured are: To minimize the swelling try to keep the bruised area elevated. If you have a bruise on your legs, avoid sitting with your feet down. You can place a pillow under the legs while lying down.
Besides the normal R.I.C.E treatments, many other simple tips are also effective in dealing with bruises:
- Massage the bruised area gently can help to reduce pain and improve circulation. However, avoid massaging the bruise if it is painful.
- Pain relief: If the bruise is painful, you can take some pain killers like Ibuprofen or Acetaminophen (Tylenol). Do not take them on empty stomach and read the leaflet carefully before use.
- Arnica and witch hazel: You can apply these tried and tested products on the bruise directly for a speedy recovery.
- Quit smoking: Cigarette and tobacco smoke makes the blood vessels more fragile and can decrease blood supply leading to a slower recovery. It is the best time to think about quitting this habit.
