Glandular fever is also referred to as infectious mononucleosis. It is a viral infection that most often occurs in the later teen years and in those who are young adults. It has been found to be more common in men than in women for unknown reasons. The infection is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, also known as EBV, which is a member of the herpes virus group of infections. So, can you answer the question"Is glandular fever contagious?" now?
Is Glandular Fever Contagious?
Yes, it is easily passed from one person to another through contact with the saliva of an individual who has been infected with the disease. It can be passed from one person to another through the following means:
- Kissing someone who has the disease. This is why some people call this condition the "kissing disease."
- Sneezing and coughing. When you cough or sneeze, you spread the virus through droplets in the air.
- Using the same eating utensils or drinking vessels of an infected person. This includes any glasses and cups.
Important Notes:
Almost everyone has already been exposed to the EBV virus when they were kids, so they are immune to catch the virus. And it has been said that most people who come in contact with this virus don't even develop infectious mononucleosis.
The incubation period for the virus, which is the time from catching the virus to developing the symptoms, is around 4-8 weeks. When a person has the infection, the period of contagion in which you can give the virus to another person lasts several weeks even after you have resolved all symptoms.
How Long Will Glandular Fever Be Contagious?
Now you have known the answer to "Is glandular fever contagious?" you may want to know when and how long will it be. According to research on this condition, about 20-80 percent of individuals who have developed infectious mononucleosis and have already recovered will still secrete Epstein-Barr virus in the saliva for many years later because of episodic reactivation of the virus in the system. However, healthy individuals may show no viral symptoms while secreting EBV during a reactivation period, so it is impossible to isolate these people who have the virus. Even though current knowledge tells us that these seemingly healthy people who are secreting EBV particles are the source of the viral transmission among the population, it is hard to tell how long the virus can be contagious.
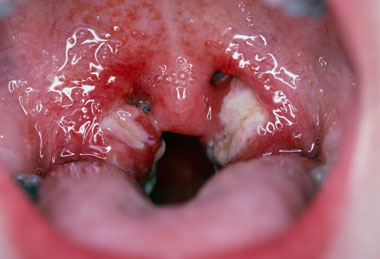
What Are the Symptoms of Glandular Fever?
If the virus is contracted by a young child, the EBV infection usually has no symptoms. Those who have symptoms tend to be older kids and young adults who come down with the disease.
Symptoms of the EBV infection include:
- Sore throat
- High fever of greater than 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit
- Extreme fatigue
- Swollen glands in the neck area
- Enlarged tonsils
- Adenoid swelling
- Purple spots located on the roof of the mouth
- Malaise or feeling generally unwell
- Headaches
- Sweating
- Chills
- A lack of appetite
- Pain around the eyes
- Splenic swelling which can show up as a lump on the side of the abdomen
- Liver swelling, which can be painful on the right side of the abdomen
- Jaundice, which shows up as a yellow coloration of the skin and eyes
Not everyone gets all of these symptoms; sore throat, fever and fatigue are the most common symptoms you will experience.
How to Diagnose Glandular Fever
Because the answer to the question "Is glandular fever contagious" is yes, you need to know what tests to do in order to diagnose the condition. There is a blood test, known as the mono spot, which checks for antibodies to the EBV virus. The mono spot test is generally considered a good test but it tends not to detect the antibodies in the first week you are having the symptoms. There are also other antibody tests for Epstein-Barr virus the doctor can use to detect the presence of the infection early on in the course of the disease. The doctor may do a complete blood count to see what your white blood cell count is. If the number of the lymphocytes in your complete blood count is elevated, this can mean you have glandular fever.
What If You Have Infected With Glandular Fever?
If you are infected with glandular fever, there are some things to keep in mind. These include the following:
1. Treat the Infection
There is no known treatment for infectious mononucleosis, but you can try to rest as much as possible and drink plenty of fluids to relieve any discomfort until recovery. It is a good idea to gargle with salt water many times in the course of the day because it helps lessen the sore throat. Because this is a viral disease, no antibiotic will be useful for its treatment. Painkillers like acetaminophen or paracetamol or NSAID therapy will help control some of the symptoms. It is important to note that you can't give aspirin to any child under the age of 16, because there is a risk of them contracting Reye's syndrome, which is a serious and sometimes deadly condition. Corticosteroids are sometimes used when there is serious swelling of the tonsils and back of the throat.
2. Prevent the Infection
If you are suffering from glandular fever, you should try to prevent spreading the disease by avoiding close contact with others who may not have had the disease before.
Don't share drinks, food utensils, or food with other people. Wash your hands frequently so you don't spread the viral particles to others. Remember that the EBV virus can be found in your mouth for many months after you recover from the infection. The virus will even remain in your system for the rest of your life, so you can shed the virus to others even when you have no symptoms. Because the virus is everywhere, there are no specific rules for avoiding the virus in teenagers or children. It is still a good idea; however, to remain in your home until you feel you have recovered from the infection.
