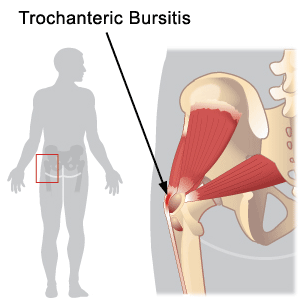
There are jelly-like sacs located around your elbow, shoulder, heel, knee and hip. They are called bursae and contain fluid. Their main purpose is to reduce friction between soft tissues and bones. You have two major bursae in your hip: one is located on the inside of your hip and is called iliopsoas bursa and the other one covers the bony point of your hipbone and is known as greater trochanter. These bursae sometimes become irritated and inflamed. The inflammation of the bursa is called bursitis, and the inflammation of the bony point of your hipbone is called trochanteric bursitis. Any inflammation of your iliopsoas bursa will also lead to pain and is referred to as hip bursitis. If you notice severe pain around the bony point of your hipbone, this could be due to trochanteric bursitis.
What Are the Symptoms of Trochanteric Bursitis?
If you're suffering from trochanteric bursitis, you will experience certain symptoms. For instance, a sharp or burning hip pain with tenderness is quite common in patients of trochanteric bursitis. Other symptoms include pain when pressing on the outside of your hip and pain with certain activities such as walking, sitting cross-less or getting out of a chair. You will have buttock pain that will often spread to your knee and outer thigh. Pain is often so severe that it disturbs your sleep. Soreness, swelling, limping and redness are some other common symptoms. Some other conditions such as sports hernia, lumbar nerve root compression, arthritis, etc., may also have similar symptoms, so it is important to talk to your doctor to identify the real cause of pain.
When to See a Doctor
In most cases, you don't need to see a doctor. Some rest will help eliminate the pain in a few weeks. However, you should go to see your doctor if you experience severe pain and soreness that interferes with your normal activities. Visit your doctor if you have recurring pain and have a fever with affected area looking red and swollen.
What Causes Trochanteric Bursitis?
A number of different factors may contribute towards the development of trochanteric bursitis. For instance:
- Any injury to the hip or simply lying on one side of your body for extended time will lead to hip pain.
- Climbing, running upstairs and standing for hours can cause overuse injury to the joint that play a role in the development of trochanteric bursitis.
- Sitting or standing maintaining an incorrect posture may also result in trochanteric bursitis and other spine problems.
- A poorly positioned bone or joint may put excessive pressure on the soft tissues, which may result in hip pain.
- Certain conditions and diseases such as gout, rheumatoid arthritis and thyroid disease may cause bursitis.
In addition, any prosthetic implants in your hip can cause pain. Some people experience pain that turns into trochanteric bursitis because calcium deposits in the tendons.
How to Treat Trochanteric Bursitis
Once you know you have developed trochanteric bursitis that's causing severe pain, you may consider talking to your doctor to work out the best treatment option. Here are some most common treatments for trochanteric bursitis.
1. Medication
Your doctor may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as naproxen, ibuprofen, celecoxibor piroxicam, to reduce pain and inflammation. Use these drugs for a short period only, and inform your doctor about any other medical condition you may have or other medications you may be using before taking NSAIDs.
2. Steroid Injection
Your doctor may give you a corticosteroid injection along with a local anesthetic to relieve severe pain. The procedure is simple and involves giving you an injection into the bursa. The injection will offer pain relief for several months, but pain may return after that, which will require another injection. Remember, however, prolonged corticosteroid injections can be damaging to the surrounding tissues.
3. Surgery
When pain is unbearable, your doctor may recommend undergoing a surgical procedure to correct any deformity to the hipbone. Surgery is usually an option when the bursae becomes thick and inflamed. Your surgeon will remove any bone spurs that may be causing pain or remove the thickened bursa to relax the large tendon of the gluteus maximu.
4. Physical Therapy
You may take advantage of physical therapy to improve your pain. Your doctor will also recommend therapy after you've undergone a surgery to improve your hip flexibility and strength. A physical therapist will explain how to stretch your hip muscles and perform certain exercises on your own. You can click HERE to learn some great exercises or watch the video below to learn some.
5. Home Care
In most cases, you can take home-care measures to reduce inflammation and manage your pain. Here are a few tips that will help you find relief from trochanteric bursitis.
- Take plenty of rest and don't engage in activities that worsen your symptoms.
- Apply an ice pack on your hip joint for 15 minutes to reduce swelling.
- Lose some weight to reduce pressure on the hip.
- Don't stand for extended hours.
- Make use of a cane or crutches to relieve pressure from your hip.
- Use a lift in your shoe to help take some pressure off from your hip.
Can Trochanteric Bursitis Be Prevented?
You can reduce your chances of developing trochanteric bursitis by maintaining a proper posture when sitting and wearing proper fitting shoes to prevent GTPS. Wear proper orthotic inserts if you have flat feet. Be sure to replace them as often as possible. Be active and train yourself to improve strength in the legs to prevent trochanteric bursitis.
