Human nervous system is very complex and is made up of spinal cord, brain, and trillions of neurons. It is responsible for performing several vital functions such as receiving the messages, interpreting them and then sending them back to the effector site. The nervous system maintains coordination with the external environment as well as with the internal organ functions. Nervous system can be divided into two major sub divisions namely central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS).
PNS comprises of nerves and neurons outside of brain and spinal cord. They coordinate with the central nervous system in receiving and sending the messages. Unlike brain and spinal cord, the nerves of PNS are not protected in any cavity or membranes, which is why peripheral nervous system is more vulnerable to develop toxic and mechanical injuries.
Components of Human Nervous System
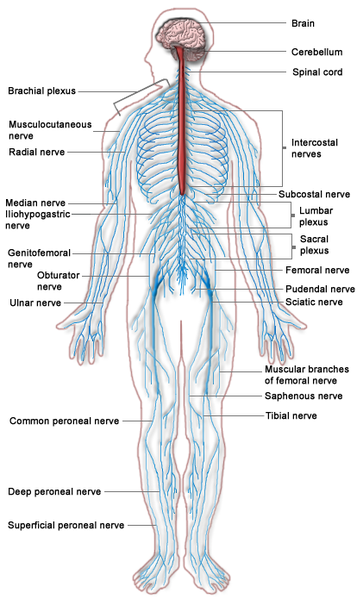 Central nervous system: Central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. It regulates the essential functions of the body such as thermoregulation, appetite control, regulation of mood, emotions and thoughts etc.
Central nervous system: Central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. It regulates the essential functions of the body such as thermoregulation, appetite control, regulation of mood, emotions and thoughts etc.- Peripheral nervous system: It consists of nerves which connects the central nervous system to the whole body. PNS is specifically composed of:
- 31 pairs of spinal nerves (attached to spinal cord)
- 12 pairs of cranial nerves (attached to cranium or skull)
In the peripheral nervous system, there are two kinds of cells. Sensory nervous cells carry information to the CNS and motor nervous cells carry information from the CNS to organs in the whole body. The motor nervous system can be further divided into two systems:
- Autonomic nervous system: It is an involuntary type of nervous system in which the body movements and actions are not regulated by self-intention. ANS primarily helps in maintaining the functions of digestive system, breathing mechanisms, heart beating etc.
- Somatic nervous system: Somatic nervous system is responsible for connecting the nerves present in the skin and muscles to the brain. These nerves produce an immediate response when stimuli are received such as a person moves his hands away as a reflex action when he touches a hot object.
Peripheral Nervous System Structure and Functions
As mentioned above, the overall function is to carry information to and from your CNS, so that normal bodily function is carried out. It helps in the regulation of many functions such as fight and flight mechanisms, voluntary and involuntary actions etc. It also controls inflammation and prepare your body for emergencies.
1. Cranial Nerves
As discussed above there are 12 pairs of cranial nerves which enter and exit through cranium. These 12 pairs are formed when motor, sensory and mixed nerves are combined. Some of the examples of cranial nerves include:
- 7th facial nerve. The motor fibers of 7th facial nerve maintain the facial expressions while the sensory fibers are responsible for carrying the taste information.
- 5th trigeminal.It has three components as described below:
- Ophthalmic: the sensory nerve supplying conjunctiva of eye, forehead, scalp and nasal mucus membrane etc.
- Maxillary: the sensory nerve supply cheeks, lower eye lids, upper teeth and gums.
- Mandibular: It’s both motor and sensory nerves. This nerve supplies lower teeth and gums, as well as lower jaw which helps in chewing of food.
2. Spinal Nerves
There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves that enters and exits from the spinal column and spread to periphery for a number of functions. The distribution of these nerves along with the function is as follows,
- Cervical plexus: It consists of 8 pairs. The nerves are supplied to shoulder, neck, and skin etc. These nerves maintain the contraction of diaphragm.
- Brachial plexus: It consists of one thoracic nerve and four cervical nerves. The nerves are supplied to skin and neck of fingertips.
- Thoracic nerves:It consists of 12 pairs. The nerves are supplied to abdominal wall and chest muscles.
- Lumbar plexus: It consists of five pairs. The nerves are supplied to lower skin, groin and thighs.
- Sacral plexus: it consists of five pairs. The nerves are supplied to hamstrings, knee and lower leg.
- Coccygeal plexus: it consists of only one pair. The nerves are supplied to skin of pelvis, anus (external sphincter) and external gentiles.
Peripheral Nervous System Disorders
Damage to peripheral nerves can cause peripheral neuropathies, which depends on the extent and severity of nerve damage and can be classified into mono and polyneuropathies. One of the very common peripheral nerve damage disease include carpel tunnel syndrome in which the nerves of wrist and hand are damaged due to excessive use.
Mononeuropathy
When only one peripheral nerve is damaged; then the condition is termed as mononeuropathy. This happens due to trauma or direct hit/compression of nerve which can lead to its damage. Sedentary living such as people who are on wheelchairs most commonly develop mononeuropathy.
Polyneuropathy
In case if more than one nerve is damaged then it is referred to as polyneuropathy. In case of multiple nerve damage, the overall functioning of the body is generally affected. Some of the common causes for polyneuropathy include body invasion through a toxin released by pathogen, toxin produced by alcohol use, renal disorders and poor diet factors etc.
Peripheral Nerve Injuries
As peripheral nerves are not protected by any membrane or hard bony structure; they are more fragile and can get damaged easily. These nerves are directly connected either with the spinal cord or brain so a minute damage to these nerves can also affect the central nervous system.
Symptoms of Peripheral Nervous System Problems
Common symptoms of peripheral nerve damage include numbness and tingling in muscles especially in the muscles of hands and feet. The damage can also be a result of any accident or trauma. In that case the person will experience loss of sensations (most probably due to nerve compression).
Treatment of Peripheral Nervous System Problems
The treatment depends on the primary cause of nerve damage. Some of the common treatment methods are listed below:
- In case the damage is caused by diabetes, controlling the blood sugar levels can significantly reduce the symptoms
- Limit alcohol consumption so that the toxin does not get accumulated in the body.
- Use of painkillers is effective in controlling the condition
- In case muscles are also involved, physical therapy is also recommended
- Pacemaker is suggested in critical conditions when the nerve damage is affecting the circulatory system.
